ether crypto symbol Understanding Its Importance and Use
Starting with the ether crypto symbol, this digital currency represents a significant pillar within the Ethereum network, shaping the landscape of decentralized finance and applications.
Ether, denoted by the symbol ETH, is not just a cryptocurrency; it plays a crucial role in facilitating transactions, powering smart contracts, and enhancing decentralized applications (dApps) on the Ethereum platform. Its influence and distinctiveness among various cryptocurrencies underscore its growing importance in the financial ecosystem.
Introduction to Ether
Ether (ETH) is the native cryptocurrency of the Ethereum network, a decentralized platform that enables developers to build and deploy smart contracts and decentralized applications (dApps). Ether plays a crucial role in this ecosystem, serving not only as a digital currency but also as "fuel" for executing transactions and computations within the Ethereum network. Unlike Bitcoin, which primarily functions as a store of value, Ether's significance lies in its utility for powering the Ethereum blockchain, facilitating transactions, and incentivizing participants to maintain the network.The creation of Ether dates back to 2015, when it was launched alongside the Ethereum blockchain by co-founders Vitalik Buterin and Gavin Wood.
Initially, Ether was distributed through a crowdsale, raising over $18 million. Since then, Ether has evolved, with numerous upgrades and enhancements that have increased its functionality and value, positioning it as one of the leading cryptocurrencies in the market today.
Understanding the Ether Crypto Symbol
The Ether crypto symbol, commonly denoted as ETH, is a standardized representation of Ether in the cryptocurrency market. This symbol is crucial for identifying Ether on various exchanges and trading platforms, simplifying transactions, and ensuring clarity among traders and investors. As Ether's popularity has grown, so has the importance of its symbol, making it a recognizable marker in the ever-expanding world of digital assets.In trading environments, the symbol ETH is used extensively, appearing on trading pairs, market charts, and wallets.
For example, when you see ETH/USD, it indicates the trading pair between Ether and the US dollar. The symbol enhances the efficiency of trading by providing a shorthand that traders can quickly understand and utilize, which is essential in the fast-paced environment of cryptocurrency trading.
Usage and Applications of Ether

Ether has a myriad of applications, primarily within the realm of decentralized applications (dApps) and smart contracts. Its utility goes beyond mere transactions, as it powers complex operations and services on the Ethereum platform. Some primary uses of Ether include:
- Transaction Fees: Ether is used to pay for transaction fees and computational services on the Ethereum network.
- Smart Contracts: Ether facilitates the execution of smart contracts, which are self-executing contracts with the terms directly written into code.
- Decentralized Finance (DeFi): Ether is a vital component in the DeFi ecosystem, enabling various financial services without intermediaries.
Industries leveraging Ether for innovative solutions range from finance to supply chain management and digital identity verification, showcasing its versatility as a digital asset.
Trading Ether
Navigating the Ether trading landscape requires a strategic approach. Here are some essential tips for effectively trading Ether:
- Research Market Trends: Stay updated with the latest market trends and news affecting Ether's price.
- Choose the Right Trading Strategy: Investors can utilize various strategies, such as day trading, swing trading, or long-term holding.
- Utilize Trading Platforms: Familiarize yourself with popular platforms like Binance, Coinbase, and Kraken for buying and selling Ether.
Understanding market psychology and having a clear investment plan can significantly enhance trading success.
Ether Wallets and Security
Storing Ether securely is paramount for investors. There are several types of wallets available for holding Ether:
- Hardware Wallets: Physical devices that store Ether offline, providing high security against hacks.
- Software Wallets: Applications that can be installed on computers or mobile devices for convenient access.
- Web Wallets: Online services that allow users to access their Ether through a browser, often with additional features.
To ensure the safety of Ether holdings, investors should implement crucial security measures such as enabling two-factor authentication, using strong passwords, and regularly updating wallet software. Transferring Ether between wallets typically involves entering the recipient's address, specifying the amount, and confirming the transaction, which is processed on the Ethereum blockchain.
Market Trends and Future of Ether
Current market trends significantly influence Ether's value. Factors such as institutional adoption, regulatory changes, and technological advancements play critical roles. For instance, the rise of decentralized finance (DeFi) has propelled demand for Ether, causing its value to fluctuate based on market sentiment and usage.Looking ahead, potential future developments for Ether include the Ethereum 2.0 upgrade, which aims to transition the network from a proof-of-work to a proof-of-stake consensus mechanism.
This shift is expected to enhance scalability and reduce energy consumption. Comparing Ether's market behavior with other major cryptocurrencies like Bitcoin and Cardano reveals unique trends influenced by Ethereum's specific use cases and community engagement.
Community and Developers Ecosystem
The Ether community is vibrant, comprising developers, enthusiasts, and contributors dedicated to the growth and evolution of the Ethereum ecosystem. Key contributors include Vitalik Buterin, co-founder of Ethereum, and other prominent developers who drive innovations and upgrades to the network.Upcoming events, including hackathons and developer meetups, foster collaboration and knowledge sharing within the community. Such gatherings are crucial for gathering feedback, which plays a pivotal role in the development and refinement of Ether and its associated technologies.
Regulatory Environment Surrounding Ether

The regulatory landscape for Ether varies globally, with different countries adopting distinct stances on cryptocurrency. For instance, while some nations have embraced cryptocurrencies, others have imposed strict regulations or outright bans. Examples of government stances include the United States, which has established a framework for regulating cryptocurrencies under various agencies, and the European Union, which is working on comprehensive regulations to oversee the crypto space.
The impact of these regulations on Ether's adoption and use is significant, as favorable regulations can spur innovation and investment, while restrictive policies can hinder growth.
Conclusion

In summary, the ether crypto symbol is more than a mere identifier; it embodies the technological advancements and potential of Ethereum. As the market evolves, understanding Ether's role and applications will be vital for investors and users alike, paving the way for innovative solutions in the cryptocurrency realm.
Questions and Answers
What does ETH stand for?
ETH stands for Ether, the native cryptocurrency of the Ethereum network.
How is Ether used in smart contracts?
Ether is used to pay for transaction fees and computational services within smart contracts on the Ethereum blockchain.
Can I buy Ether with traditional currencies?
Yes, Ether can be purchased using traditional currencies on various exchanges that accept fiat transactions.
What are the main types of wallets for Ether?
Ether can be stored in software wallets, hardware wallets, and paper wallets, each offering varying levels of security.
Is Ether subject to regulation?
Yes, Ether is subject to regulations that may vary by country, impacting its use and trading practices.






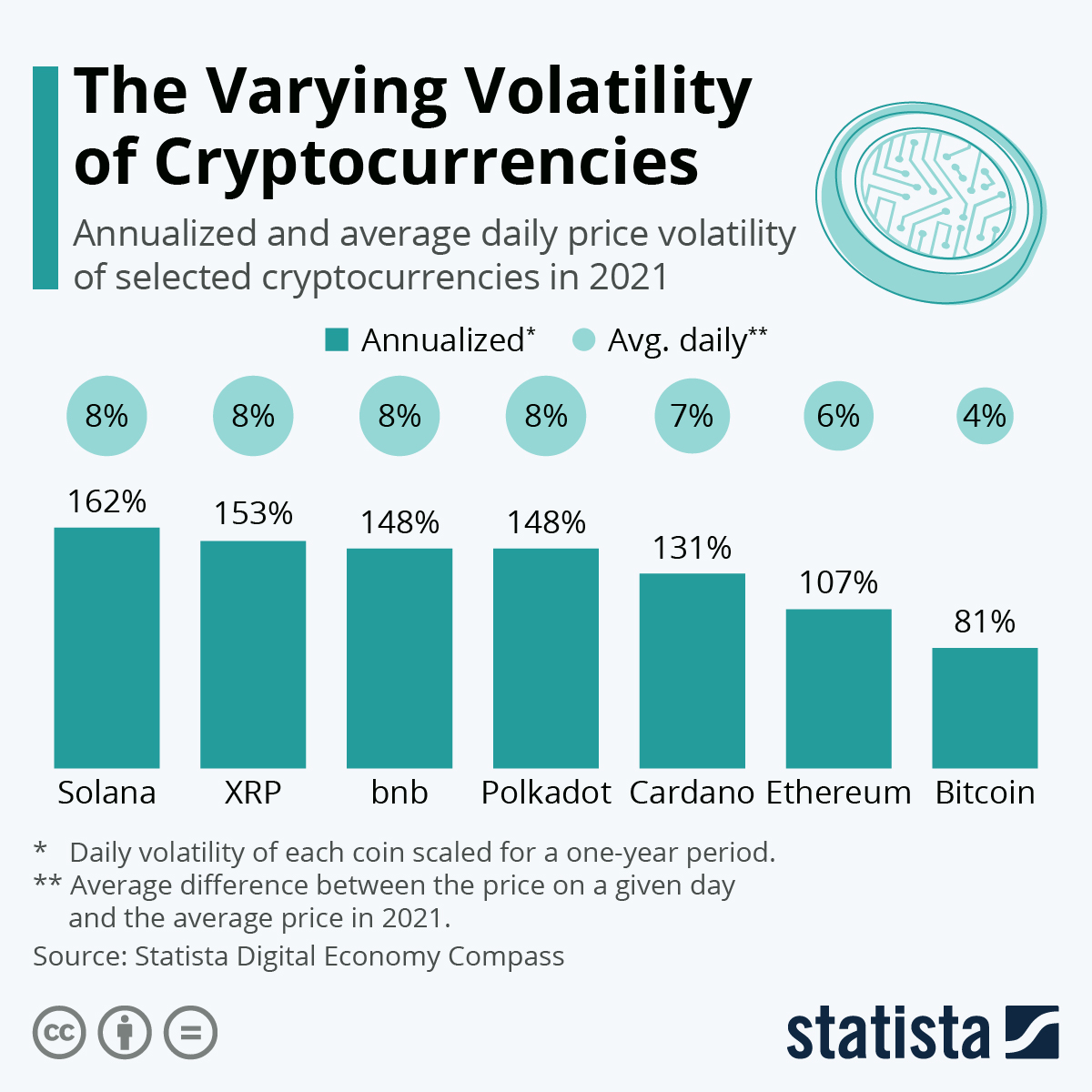



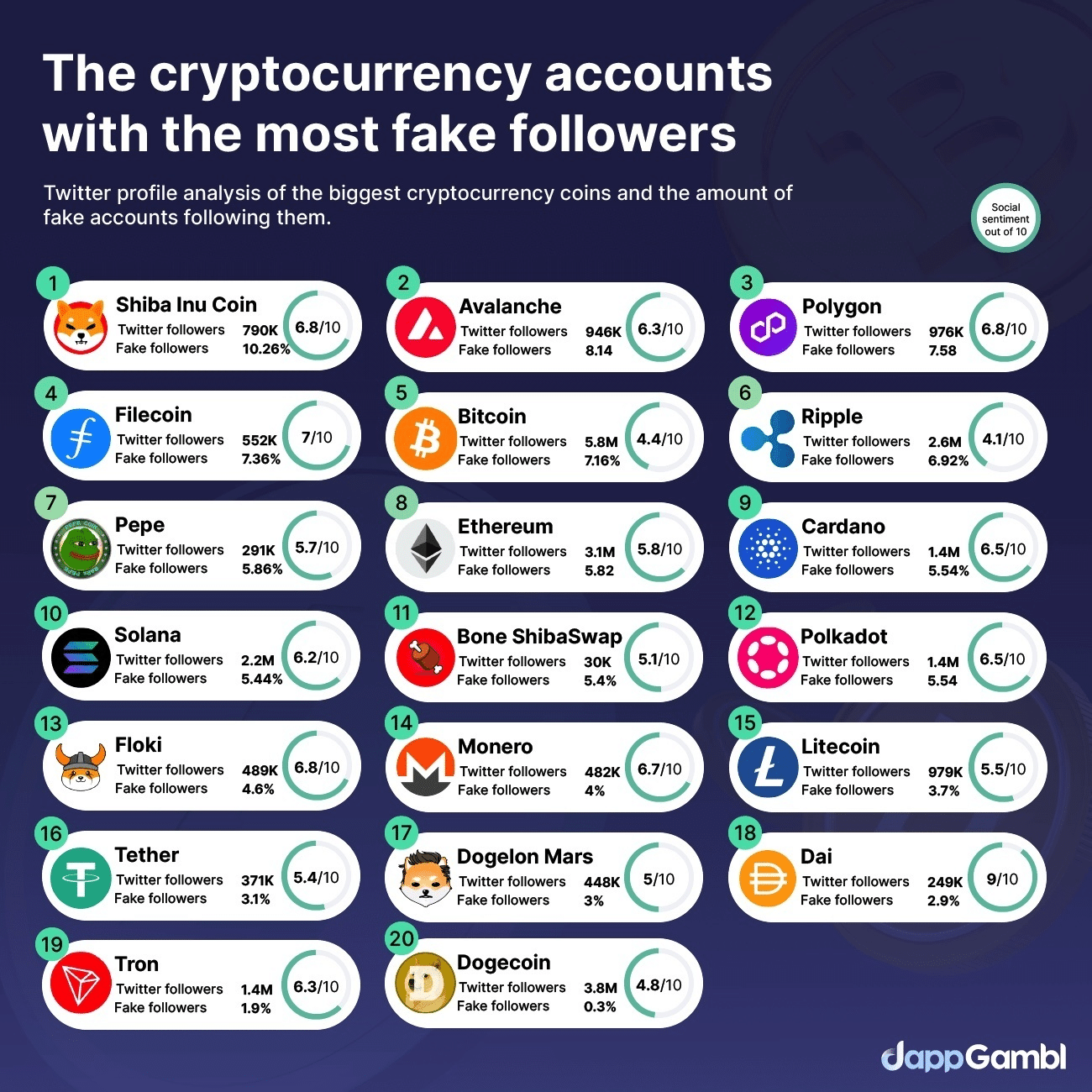

 10%
10% 5%
5% 0%
0%